High-Grade Glioma Cancer
Nimotuzumab usage resulted in better progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for newly diagnosed EGFR-positive GBM patients. [1]
Demonstrated a notably extended PFS
Nimotuzumab + RT + TMZ
12.4 Months
(95% CI, 7.8-17.0)
vs
RT + TMZ
8.2 months
(95% CI, 6.1-10.3)
PFS : progression free survival ; mOS = median overall survival;
HR = hazard ratio; CI = confidence interval
Demonstrated a notably extended mOS
Nimotuzumab + RT + TMZ
27.3 Months
(95% CI, 19.0-35.6)
vs
RT + TMZ
16.7 months
(95% CI, 11.1-22.2)
PFS : progression free survival ; mOS = median overall survival;
HR = hazard ratio; CI = confidence interval
Nimotuzumab for Glioblasma (GBM)
Below is a summary of Phase III clinical trials of Nimotuzumab in GBM, conducted by She, L. et al. (2022) and titled “Radiotherapy Plus Temozolomide With or Without Nimotuzumab Against the Newly Diagnosed EGFR-Positive Glioblastoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study”
Study Background & About GBM
Glioblastoma (GBM), the most common primary brain tumor in adults (approximately 60%-70% of gliomas), is highly aggressive with a poor prognosis.2 Current treatment methods, including surgery, chemoradiotherapy, and chemotherapy, offer limited improvements in progression-free survival (PFS) to 6.9 months and overall survival (OS) to 14.6 months. Even with regular treatment, GBM patients with unmethylated O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter have a worse prognosis.3 To enhance survival, clinical studies exploring combination therapies involving targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and other drugs are underway, but few have shown significant benefits. Therefore, there is a pressing need to discover novel treatments for GBM.
Read More
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is present in more than 40% of gliomas and is associated with tumor growth, invasion, and resistance to treatment.4 Nimotuzumab, a monoclonal antibody against EGFR, inhibits EGFR signaling, promotes immune-mediated cytotoxicity, and enhances drug and radiotherapy sensitivity.5 While theoretical evidence suggests it could improve overall survival (OS) in primary GBM, clinical consensus is lacking. Studies have yielded mixed results. In some cases, nimotuzumab improved OS and progression-free survival (PFS), especially in patients with EGFR amplification.
However, not all studies showed significant benefits, and further research is needed to establish its efficacy, especially in EGFR-positive GBM. This retrospective cohort study in China aims to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and safety of nimotuzumab combined with concurrent irradiation and TMZ in newly diagnosed EGFR-positive GBM patients, accounting for various prognostic factors.
Study Design

Efficacy
Progression Free Survival
According to this single-center, retrospective, cohort study in China, nimotuzumab combined with CCRT displayed superior efficacy in patients with newly diagnosed EGFR-positive GBM, particularly those with unmethylated MGMT promoter.
The median PFS was 12.4 months (95% CI, 7.8-17.0) and 8.2 months (95% CI, 6.1-10.3) in the 2 groups, respectively, P = .052.

Overall Survival
The median OS was 27.3 months (95% CI, 19.0-35.6) and 16.7 months (95% CI, 11.1-22.2), respectively, P = .018.
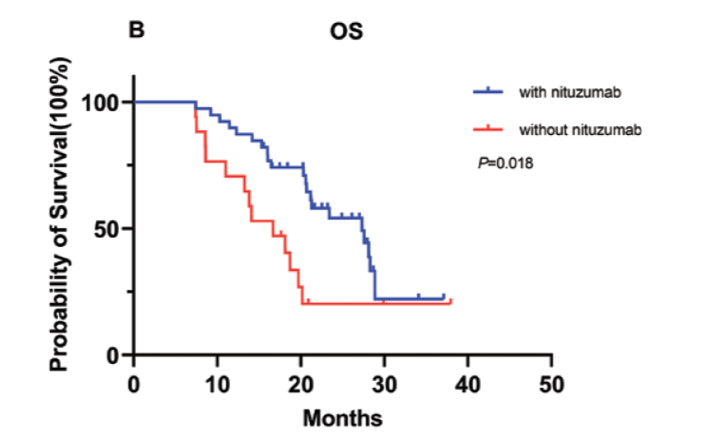
Progression Free Survival and Overall Survival
In individuals lacking methylation in the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter, those who received nimotuzumab treatment experienced notably improved PFS and OS compared to those who did not receive nimotuzumab.
(median PFS: 19.3 vs 6.7 months, P = .001; median OS: 20.2 vs 13.8 months, P = .026).

Safety Profile
During the treatment period, no statistically significant difference in toxicity was detected between the 2 groups. Nimotuzumab combined with standard TMZ + RT was safe.
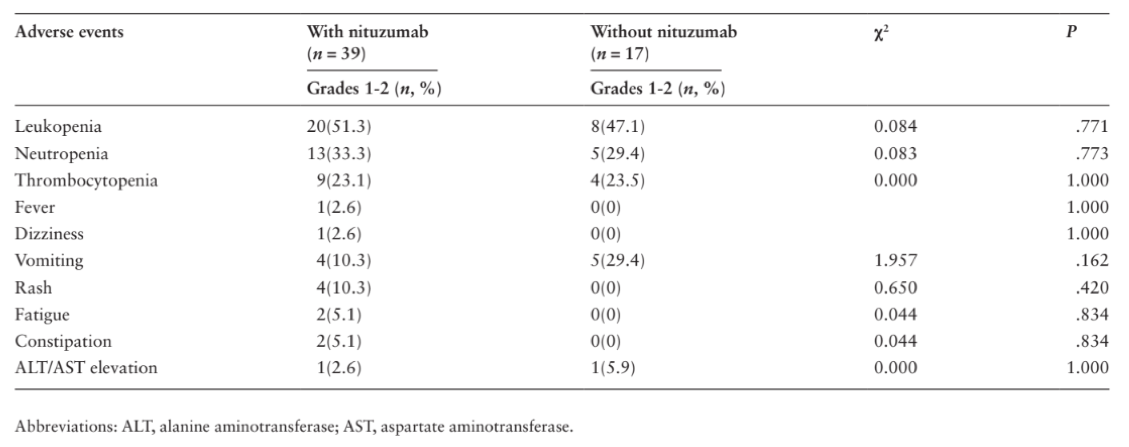
Conclusion
This retrospective cohort analysis demonstrates that Nimotuzumab in combination with concurrent RT with TMZ is effective in patients with newly diagnosed EGFR-positive GBM, particularly those with an unmethylated MGMT promoter. Furthermore, nimotuzumab was found to be safe and tolerable.
Reference
- She, L., Gong, X., Su, L., & Liu, C. (2023). Radiotherapy Plus Temozolomide With or Without Nimotuzumab Against the Newly Diagnosed EGFR-Positive Glioblastoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study. The oncologist, 28(1), e45–e53.
- Wen PY, Kesari S. (2008). Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med.,359(5):492-507.
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. (2005). Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med.,352(10):987-996.
- Huang PH, Xu AM, White FM. Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci Signaling. 2009;2(87):re6.
- Ramos TC, Figueredo J, Catala M, et al. Treatment of high-grade glioma patients with the humanized anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody h-R3: report from a phase I/II trial. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5(4):375-379.
